BioCycle November 2006, Vol. 47, No. 11, p. 13
Washington, D.C.
ENERGIZING RECYCLING
At its annual Congress in Atlanta last month, the National Recycling Coalition (NRC) announced a historic partnership with the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) and major food and beverage manufacturers and suppliers to reignite American consumers’ interest in recycling by providing clear, consistent information on what, how, and why to recycle.
“This partnership is an unprecedented gathering of recycling advocates, leading trade associations, and government agencies that will breathe new life into the recycling movement,” says Kate Krebs, NRC’s executive director. “Although many private and public sector organizations communicate with consumers about recycling now, sometimes consumers get mixed messages about how and what to recycle. This new campaign will coordinate those independent activities, combine financial resources, and leverage the vast marketing power of all of the campaign’s partners to encourage consumers and private companies to recycle more.”
NRC, EPA, the American Beverage Association, the Food Marketing Institute, the Grocery Manufacturers Association/Food Products Association, and the International Bottled Water Association, which combined represent the manufacturers and suppliers of America’s most popular brands, serve as founding members of the partnership. Adds Krebs: “Our current research shows that Americans have lost their sense of urgency about recycling. This campaign will remind Americans why recycling is as important as ever, and take our nation’s recycling participation to the next level.” The partnership will develop and disseminate consumer-friendly recycling icons (such as the familiar chasing arrows symbol) and accurate and standardized recycling terminology for use in product advertising and product labeling.
Toronto, Ontario, Canada
CALL FOR PAPERS – COMPOSTING IN CANADA
The Composting Council of Canada issued a Call for Papers for its 17th Annual National Composting Conference in Moncton, New Brunswick, September 19-21, 2007. Papers on the following topics are encouraged: Compost marketing strategies (high volume markets vs. high value broker options); compost technology developments; operational issues including odor control; education and communication strategies; regulations and standards; analytical and applied composting research; program implementation; and special waste composting including on-farm, manure management, wood and paper fiber wastes, biosolids and food residuals. A one page abstract and short biography should be submitted to The Composting Council of Canada, 16 Northumberland St., Toronto, ON M6H 1P7; www.compost.org; 416-535-0240.
Federal Way, Washington
PETE GROGAN NAMED RECYCLER OF THE YEAR
Recycling pioneer Pete Grogan received the Lifetime Achievement Award and 2006 Recycler of the Year Award by the National Recycling Coalition at NRC’s annual conference in October. Grogan, Recycling Market Development Manager at Weyerhaeuser, Inc., has been at the forefront of the recycling industry for 30 years. He began his involvement with recycling in Boulder, Colorado in 1976 with the founding of an organization called Eco-Cycle, which still thrives today. Since that time, Grogan has been involved with recycling initiatives around the world, helping communities start programs. He was nominated for the award by Jack DeBell of the University of Colorado’s recycling services. “Pete has been a leader in advocating for recovering more recyclables as a way of boosting environmental and financial benefits for all sectors of society,” said James R. Keller, Weyerhaeuser senior vice president, Containerboard Packaging and Recycling.
Manitowoc County, Wisconsin
COMPANY RECEIVES STATE GRANT TO HELP DEVELOP BIODIESEL INDUSTRY
Wisconsin Agriculture Secretary Rod Nilsestuen awarded a grant of $97,500 to Quality Roasting, Inc. of Valders to more than double its capacity to generate soybean oil, a raw material used to produce biodiesel. “Developing the state’s biodiesel industry boosts the local economy and protects the environment,” declared Nilsestuen. “We need to depend more on the Midwest and less on the Mideast,” added Wisconsin Governor Jim Doyle.
Founder of Quality Roasting, Scott Rabe, anticipates that by 2008, his soybean crushing facility will need approximately 1.5 million bushels of soybeans annually to produce 1.15 million gallons of soybean oil. That amount can be used to generate approximately 1.4 million gallons of biodiesel. Nearly all soybean purchases come from grain grown in Wisconsin. “The 1.5 million bushels to fill capacity would be valued at slightly more than $8.1 million,” he estimated. Value of soybeans in the East Central region of Wisconsin is expected to increase by 5 to 10 cents/bushel as a result of the project.
Current biodiesel production in Wisconsin is estimated at around two million gallons. Grant funds for the Valders project came from the state’s first-ever Biobased Industry Opportunity (BIO) grant program.
In late September, Governor Doyle described plans to grow bioindustry and renewable energy in Wisconsin through a $450 million public and private investment strategy including nearly $80 million from the state. It’s part of a broader effort to create 17,000 jobs. The plan included financial incentives such as bonds, tax credits, loans and grants for companies to invest in and develop new technologies and renewable energy.
“The new state funding will encourage energy technologies designed to kick our addiction to oil,” added Doyle. The plan includes: Wisconsin Energy Independence Fund – $50 million in loan guarantees plus leveraging $100 million in private sector support. This will help achieve the Governor’s goal of generating 25 percent of electricity and 25 percent of transportation fuel from renewables by 2025; Wisconsin Energy Independence Tax Incentives – tax credits for gas stations to invest in E-85, biodiesel tanks and pumps; Wisconsin Energy Independence Grant Program – $20 million in grants for companies and researchers creating technologies to increase renewable fuels; Investment would leverage $240 million from private investors.
Plymouth, England, UK
CHARACTERIZING FOOD, GREEN WASTE FEEDSTOCKS FOR COMPOSTING
The September 2006 issue of Warmer Bulletin summarizes a research project examining in-vessel composting of food wastes at the University of Plymouth in the United Kingdom. The research focused on characterizing food and green waste feedstocks to determine levels of pathogens, nutrients and potentially toxic elements. Contamination and plant response in greenhouses were also examined, with final data checked against quality composts. Two main field sites used forced aeration systems, composting under a UK standard for catering residuals.
Composted food wastes met all requirements for pathogen and potentially toxic element levels, with the exception of a single batch that exceeded limits for nickel. Nutritionally, composted food wastes contained higher concentrations of nitrogen than composted green wastes. Cardboard was the most significant physical contaminant of food waste composts.
Food waste feedstocks contained higher concentrations of nitrogen and phosphorus than green waste and mixed green/cardboard feedstocks. Combined with its contaminant effects, use of mixed cardboard with food or green wastes as a feedstock cannot be recommended. Topsoil, peat-free and loam-based composts commanded a premium in the region; all could provide value-added outlets for composted food wastes.
For more details, contact Richard Shepherd at the University of Plymouth in Devon; e-mail: rashepherd@plymouth.ac.uk. The full report on organic waste treatment using novel composting technologies is available at www.science.plym.ac.uk.
Trenton, New Jersey
LIQUID PLANT FOOD FROM WORM CASTINGS WINS ECOFRIENDLY PRODUCT AWARDS
TerraCycle, manufacturer of liquid plant fertilizers brewed from vermicompost and packaged in reused soda bottles, has been honored by two national environmental groups. Zerofootprint and the Clean Air Foundation have both identified TerraCycle’s products as “The Most Eco-Friendly Product available today.” Notes a press release announcing the awards: “Unlike the production of any other consumer product, which produces waste, TerraCycle actually consumes waste in manufacturing their product. TerraCycle’s plant foods are the world’s first product that is made from (worm poop) and packaged (used soda bottles) entirely in waste!” To date, the company has reused over 1.2 million bottles that have been collected by over 1,600 schools, churches and other community groups across North America. The liquid fertilizer is carried by major retailers including Wal-Mart, Home Depot, CVS and Whole Foods. In 2007, TerraCycle will be launching 10 new products, including lawn and garden fertilizers (also packaged in reused bottles), a line of Peat-Free potting mixes packaged in reused milk jugs and “worm poop” Organic Seed Starters will come in a tray made from 100 percent recycled paper.
Lancaster, Pennsylvania
COUNTY SOLID WASTE AUTHORITY JOINS CHICAGO CLIMATE EXCHANGE
The Lancaster County Solid Waste Management Authority (LCSWMA) has become the first public environmental services organization in the United States to join the Chicago Climate Exchange (CCX), the first legally-binding, multisector market for reducing and trading greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions. The LCSWMA warrants inclusion in the CCX due to the greenhouse gases generated by its 1,200 tons/day waste-to-energy facility and collection trucks. As a member, LCSWMA has committed to demonstrating a six percent reduction in those emissions as measured between the baseline year of 2000 and the deadline of 2010.
All emissions data must be verified by NASD, CCX’s provider of regulatory services. LCSWMA operates an integrated solid waste management system that primarily serves Lancaster County. The system handles approximately 575,000 tons of waste/per year. There is a 2,000 tons/day sanitary landfill and a 3.2 megawatt landfill gas-to-energy plant owned and operated by PPL, a regional electric utility. The landfill gas recovery and waste-to-energy facilities generate enough renewable energy to power one out of five homes in the county. The county-wide recycling program has achieved a 39 percent recycling rate.
CCX-approved verifiers have already certified the Authority’s landfill gas system and verified that over 35,500 metric tons of CO2 equivalents have already been destroyed since the gas-to-energy plant began operation in February 2006. “The Authority has been and remains committed to actively pursuing environmentally sound and productive methodologies to manage municipal solid waste,” says Jim Warner, Executive Director of LCSWMA. “Joining the CCX provides us a platform to extend our best environmental practices to reducing greenhouse gas emissions. Being both a member and a greenhouse gas offset project participant with CCX enables us to achieve environmental goals with financial rewards attached. That’s an attractive combination for any organization.” For more details, visit the Authority’s website: www.lcswma.org.
Richmond, Virginia
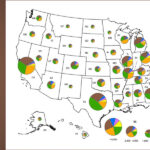
2005 RECYCLING RATES REPORTED
The Virginia Department of Environmental Quality (DEQ) has completed its review of the recycling rate data reported for calendar year (CY) 2005. Data for this summary report was compiled from reports submitted by the 74 solid waste planning units (SWPU) and represents recycling information from all 325 Virginia cities, counties and towns. In some cases, reported data was adjusted for consistency with the Virginia Solid Waste Planning Regulation. From the data, DEQ has calculated a statewide average recycling rate for CY 2005 of 32.2 percent, based on 2,757,442 tons of material recycled, and 8,554,784 tons of waste generated. (In CY 2004, the statewide average recycling rate was 29.8 percent.) Forty-five of the 74 SWPUs reported recycling rates of 25 percent or greater; most of the higher recycling rates were reported in the urban areas of Virginia.
In reviewing the statewide totals from the recycling rate reports, there was a two percent increase from CY 2004 in the principal recyclable materials – paper, metals, plastics, etc. – and an 11 percent increase over CY 2004 in supplemental recyclable materials, e.g., waste tires, used oil, electronics and C&D debris. MSW disposed decreased by eight percent. The 2005 report can be downloaded at: www.deq.virginia.gov/recycle. Click on “The Virginia Annual Recycling Rate Report for CY 2005 now available” link.
St. Paul, Minnesota
NATION’S 1,000TH E85 STATION OPENS IN SMALL ALTERNATIVE SITE
According to the National Ethanol Vehicle Coalition, the nation’s 1,000th station selling alternative fuel E85 opened up in Bemidji in northern Minnesota. “We’ve had so many stations opening lately that determining which site is the 1,000th E85 outlet in the United States is a challenge,” says a member of a public/private partnership that promotes E85 use. “It might just as easily been in St. Louis Park, Rochester or Duluth. Many flex-fuel vehicle owners now have a station near them and that’s really boosting sales.” Minnesota has nearly 300 outlets selling an estimated 2.3 million gallons monthly. E85 is a blend of up to 85 percent ethanol and 15 percent gasoline.
Eastern Shore, Maryland
SUSTAINABLE AGRICULTURE AWARDS FOR 2006 GO TO MARYLAND LIVESTOCK FARMS
At their farm near Chestertown, Maryland, Edwin and Marian Fry milk 250 cows and raise 225 replacement heifers annually as they spread dairy manure on crop fields. This summer, they also won the Patrick Madden Award for Sustainable Agriculture. “The award is SARE’s way of encouraging a whole farm approach to agriculture,” says Fred Magdoff, Northeast SARE regional coordinator. “We look for farmers who see their farms as a natural, complex system and use that understanding to become profitable and sustainable.” Add the Frys: “As part of an American farming tradition, we have strong values associated with land stewardship and the addition of food. … We help consumers recognize that healthy food comes from healthy earth.”
November 22, 2006 | General